경희대학교 박제만 교수님의 자료구조 수업을 기반으로 정리한 글입니다.
Exercise #1
Problems
- Implement rotateFirstItem() in Circular Queue with Reserved space.
- This function "ROTATES" the first item of the queue.

▶ Both are OKAY (in-place or not)!
HINT: It is allowed to call "other member functions" inside a member function.
- e.g., enqueue(), dequeue(), isEmpty(), etc.)
template<class ItemType>
void QueueType<ItemType>::rotateFirstItem()
{
if(isEmpty()){
return;
}
enqueue(dequeue());
}▶ rotateFirstItem()
Exercise #2
Problems
- Implement MazeExplorer() function that finds the path from "entry to "exit" in the maze.
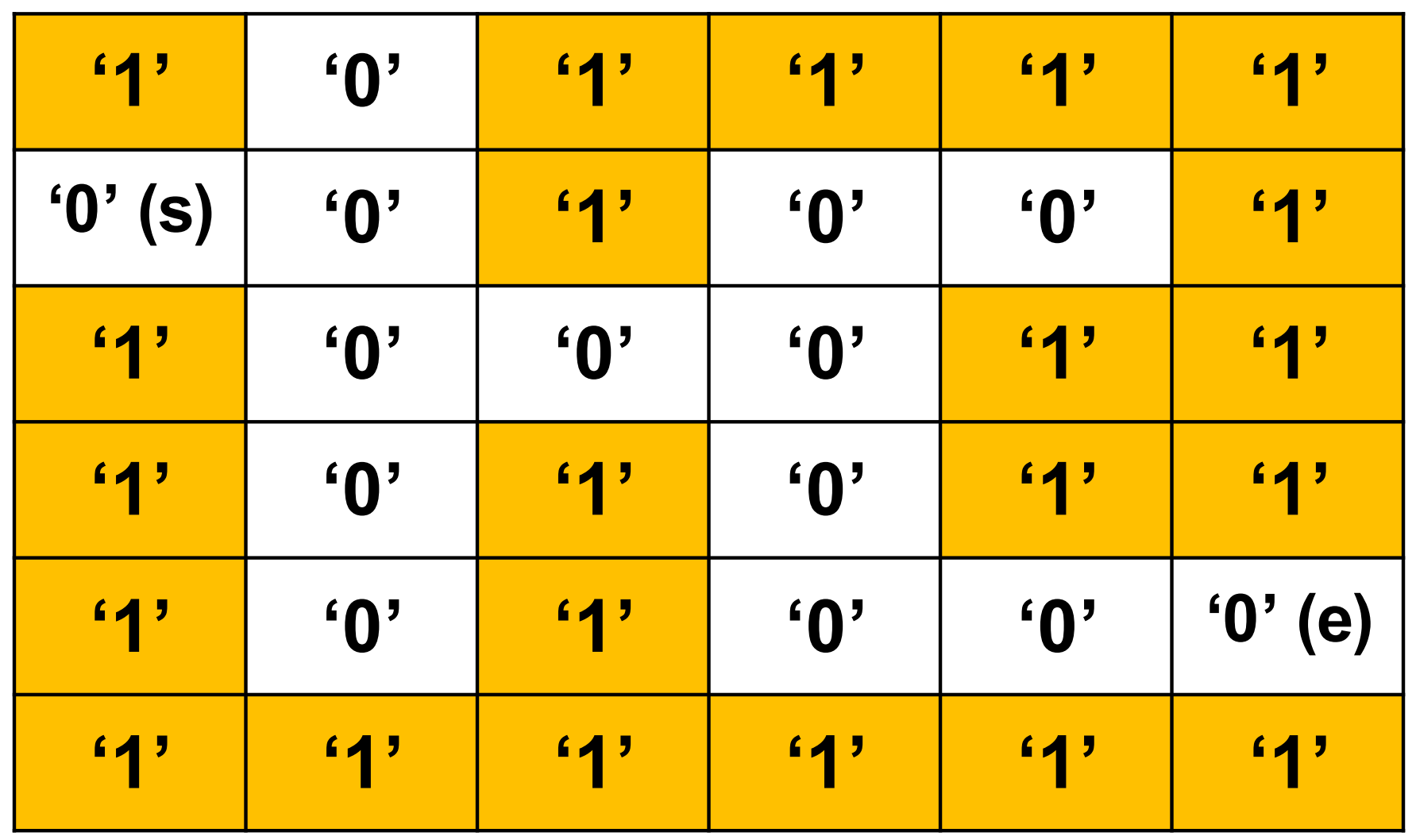
▶ Maze is 2D char array
- '1' means the wall
- '0' means the empty space
- location entry(1,0); / location exit(4,5);
mazeExplorer() uses QUEUE to maintatin the trace of traversal(여행).
- Print the visited coordinate(좌표).
- Start with "entry" enqueue all adjacent(인접한) "empty space" into QUEUE.
- Dequeue from QUEUE and repeat.
Priority of visiting
- Upward -> rightward -> downward -> left ward
Correct Outputs: path founds -> return true / EMPTY queue, NOT found -> return false
- [1][0]
- [1][1]
- [0][1]
- [2][1]
- [2][2]
- [3][2]
- [2][3]
- [4][2]
- [1][3]
- [3][3]
- [1][4]
- [4][3]
- [4][4]
- [4][5]
mazeExplorer():
- Prints all visited points in order ([ ] [ ] format).
- you can use printLocation() function to print.
- Returns true if there is a route from "entry" to "exit".
- Returns false if there is no route from "entry" to "exit".
bool mazeExplorer(char map[][MAZE_SIZE], location entryPoint, location exitPoint){
QueueType<location> tempQueue(20);
tempQueue.enqueue(entryPoint);
map[entryPoint.row][entryPoint.col] = '.';
int dRow[] = { -1, 0, 1, 0 };
int dCol[] = { 0, 1, 0, -1 };
while (!tempQueue.isEmpty()) {
location current = tempQueue.dequeue();
printLocation(current);
if (current.row == exitPoint.row && current.col == exitPoint.col) {
return true;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int newRow = current.row + dRow[i];
int newCol = current.col + dCol[i];
if (newRow >= 0 && newRow < MAZE_SIZE && newCol >= 0 && newCol < MAZE_SIZE && map[newRow][newCol] == '0') {
map[newRow][newCol] = '.';
tempQueue.enqueue(location(newRow, newCol));
}
}
}▶ mazeExplorer() - v1
bool mazeExplorer(char map[][MAZE_SIZE], location entryPoint, location exitPoint){
QueueType<location> tempQueue(20);
tempQueue.enqueue(entryPoint);
while(!tempQueue.isEmpty()){
location cur = tempQueue.dequeue();
int cur_row = cur.row;
int cur_col = cur.col;
printLocation(cur);
map[cur_row][cur_col] = '.';
if(cur_row == exitPoint.row && cur_col == exitPoint.col){
return true;
}
else{
if(map[cur_row-1][cur_col] == '0'){
tempQueue.enqueue(location(cur_row-1, cur_col));
}
if(map[cur_row][cur_col+1] == '0'){
tempQueue.enqueue(location(cur_row, cur_col+1));
}
if(map[cur_row+1][cur_col] == '0'){
tempQueue.enqueue(location(cur_row+1, cur_col));
}
if(map[cur_row][cur_col-1] == '0'){
tempQueue.enqueue(location(cur_row, cur_col-1));
}
}
}
return false;
}▶ mazeExplorer() - v2 (solution)
Exercise #3
Problems
- Implement priority_dequeue() in Circular Queue with Reserved space.
- This function returns the "task" that has the minimum priority in the queue.
- The order of items in the queue must be kept.

▶ Both approaches are OKAY!
template<class ItemType>
bool QueueType<ItemType>::priority_dequeue(ItemType& ret) {
if(isEmpty()){
cout << "[ERROR] Queue is Empty. Dequeue Failed." << endl;
return false;
}
int minIndex = (front + 1) % maxQueue;
int minPriority = data[minIndex].priority;
for (int i = (front + 1) % maxQueue; i != (rear + 1) % maxQueue; i = (i + 1) % maxQueue) {
if (data[i].priority < minPriority) {
minPriority = data[i].priority;
minIndex = i;
}
}
ret = data[minIndex];
for (int i = minIndex; i != rear; i = (i + 1) % maxQueue) {
data[i] = data[(i + 1) % maxQueue];
}
rear = (rear - 1 + maxQueue) % maxQueue;
return true;
}▶ priority_dequeue() - v1
template<class ItemType>
bool QueueType<ItemType>::priority_dequeue(ItemType& ret) {
if(isEmpty()){
cout << "[ERROR] Queue is Empty. Dequeue Failed." << endl;
return false;
}
int searching_index = front;
int min_id = -1;
int min_val = 99999;
do{
searching_index = (searching_index + 1) % maxQueue;
if(data[searching_index].priority < min_val){
min_id = searching_index;
min_val = data[searching_index].priority;
}
} while(searching_index != rear);
ret = data[min_id];
int copy_index = min_id;
int next_index;
while(copy_index != rear){
next_index = (copy_index + 1) % maxQueue;
data[copy_index] = data[next_index];
copy_index = next_index;
}
if(rear == 0){
rear = maxQueue - 1;
}
else{
rear --;
}
return true;
}▶ priority_dequeue() - v2 (solution)
'CS > 자료구조' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Programming Exercise: Lab #4 (1) | 2025.04.19 |
|---|---|
| Chapter 5: Linked Structures (1) (0) | 2025.04.16 |
| Chapter 4.5: Programming Tips (0) | 2025.04.16 |
| Programming Exercise: Lab #2 (1) | 2025.04.06 |
| Chapter 4: Queue (0) | 2025.03.31 |