경희대학교 박제만 교수님의 자료구조 수업을 기반으로 정리한 글입니다.
Linked Structure
Array-based Stack Implementation

▶ In the previous implementation, we consider an entire stack (a set of items) as a single object (array).
New stack Implementation

▶ Here, we consider each item in the stack a single object (Node).
- How could we define relationships between items? (Who's on top of whom?)
Node Implementation
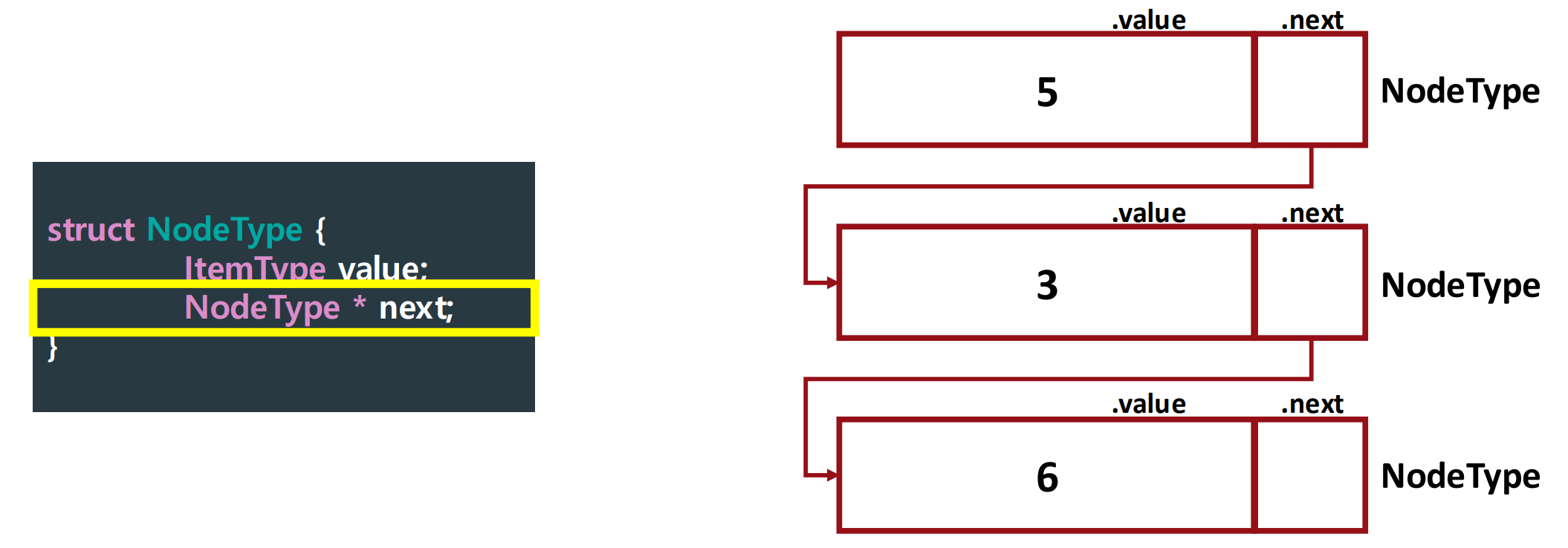
▶ A pointer can be used for it!
- The pointer named 'next' will point to the next 'NodeType'.
We call it "linked structures".
Each node has a value and a pointer pointing to the next node.

▶ We need another pointer to indicate the top of the stack.
Why We Need topPtr?
All variables have their own name and memory space.
Computers use these variable names to access each memory space.
Dynamically allocated memory spaces do not have bound(결속된) names.
- 변수 이름 없이 포인터를 통해 접근, 이때 동적할당된 공간에 포인터가 없는 경우 메모리 누수가 발생한 것임.
A dynamically allocated variable needs a pointer to be accessed.
All but the first (top) node is pointed to by other pointers. (포인터 없으면 변수에 접근 불가)
topPtr points to the top node.
- 포인터 없으면 변수에 접근 불가, 때문에 top node를 가리키는 topPtr 필요
Stack Definition using Node
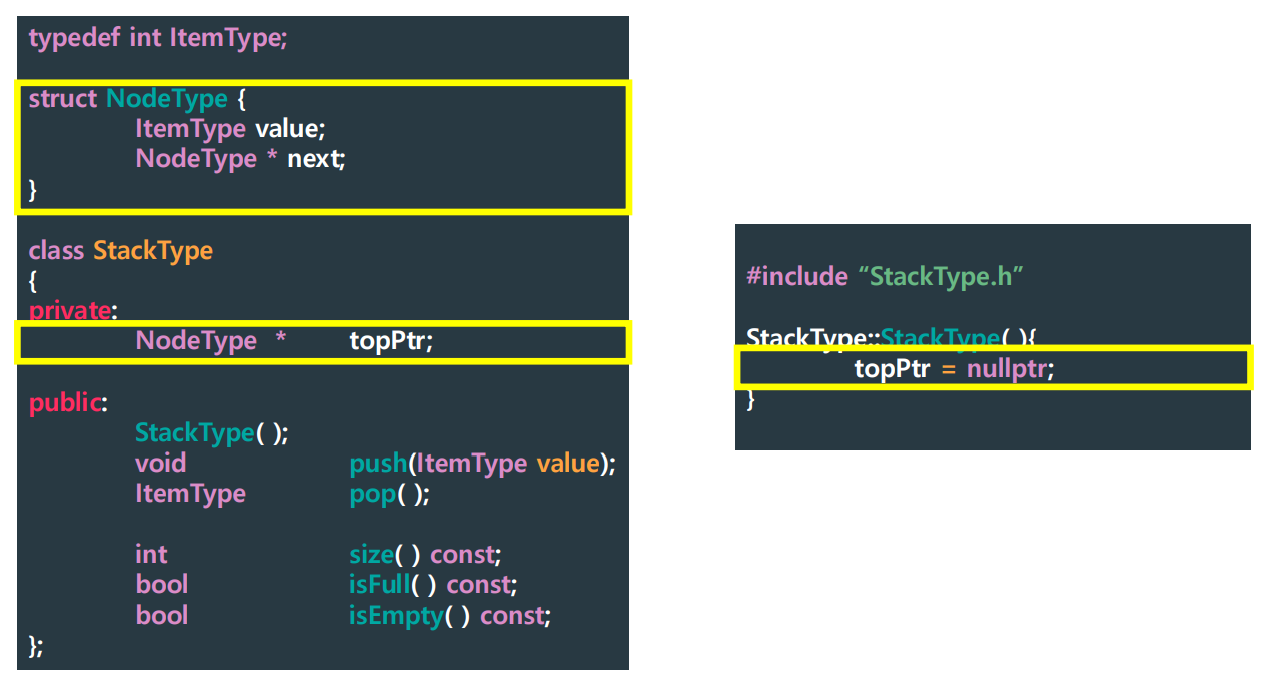
▶ Implementation Level
Tracing Client Code


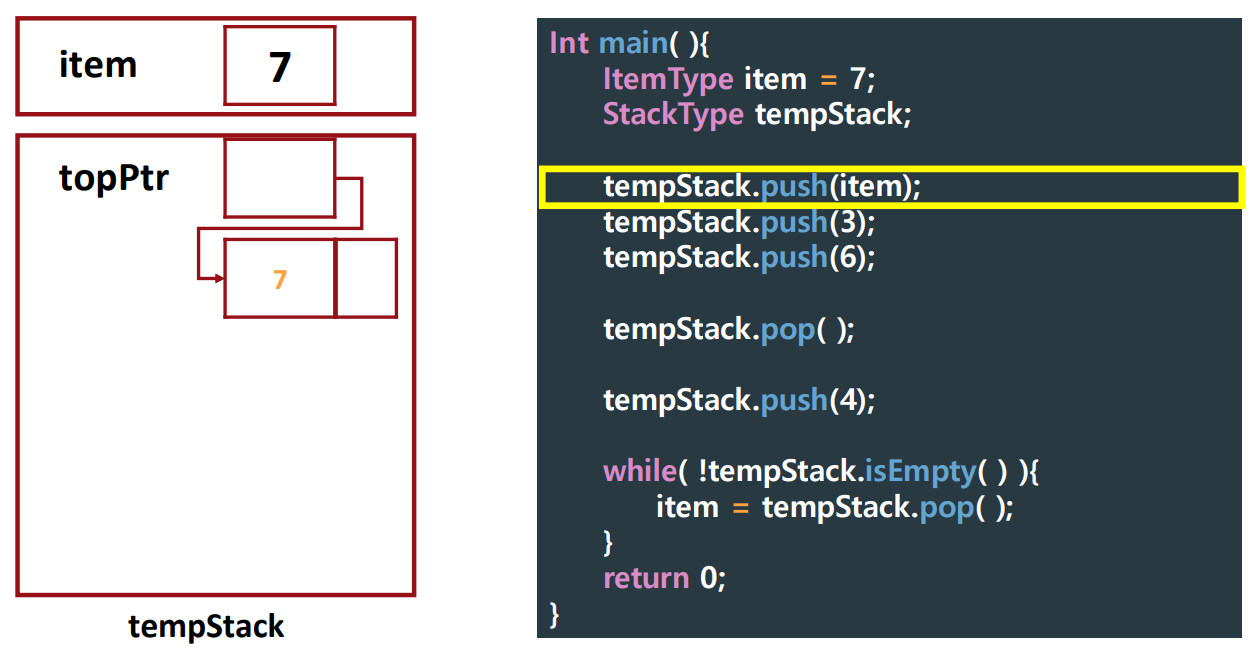



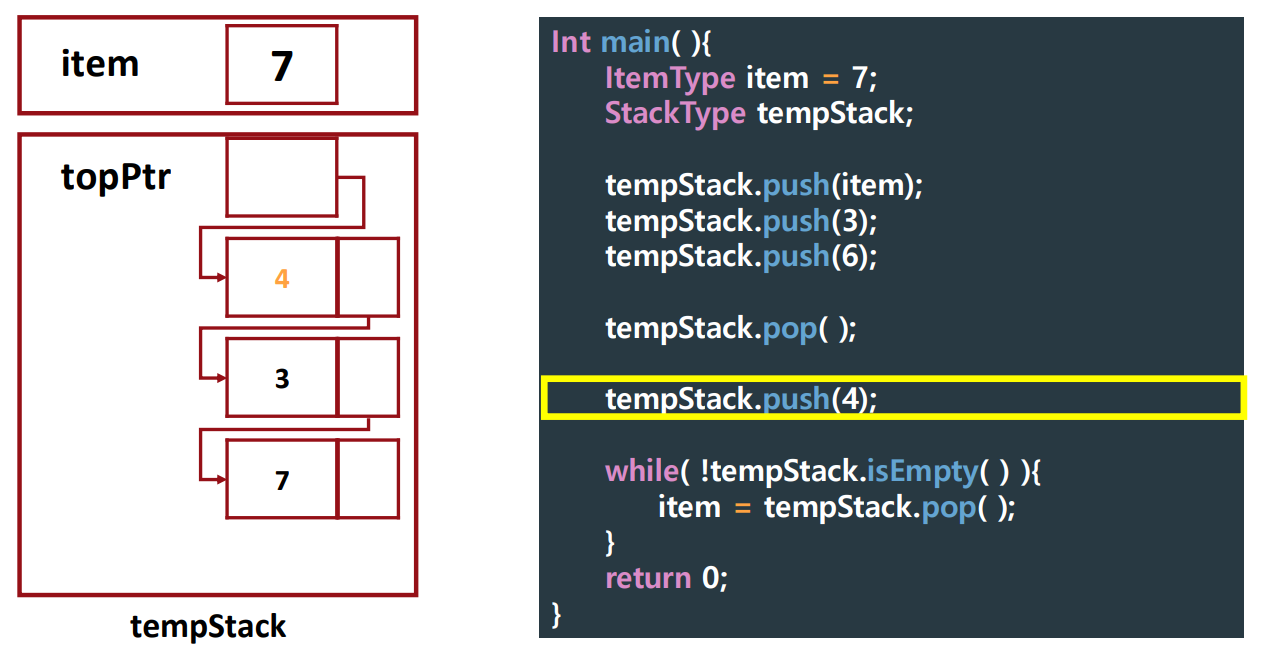
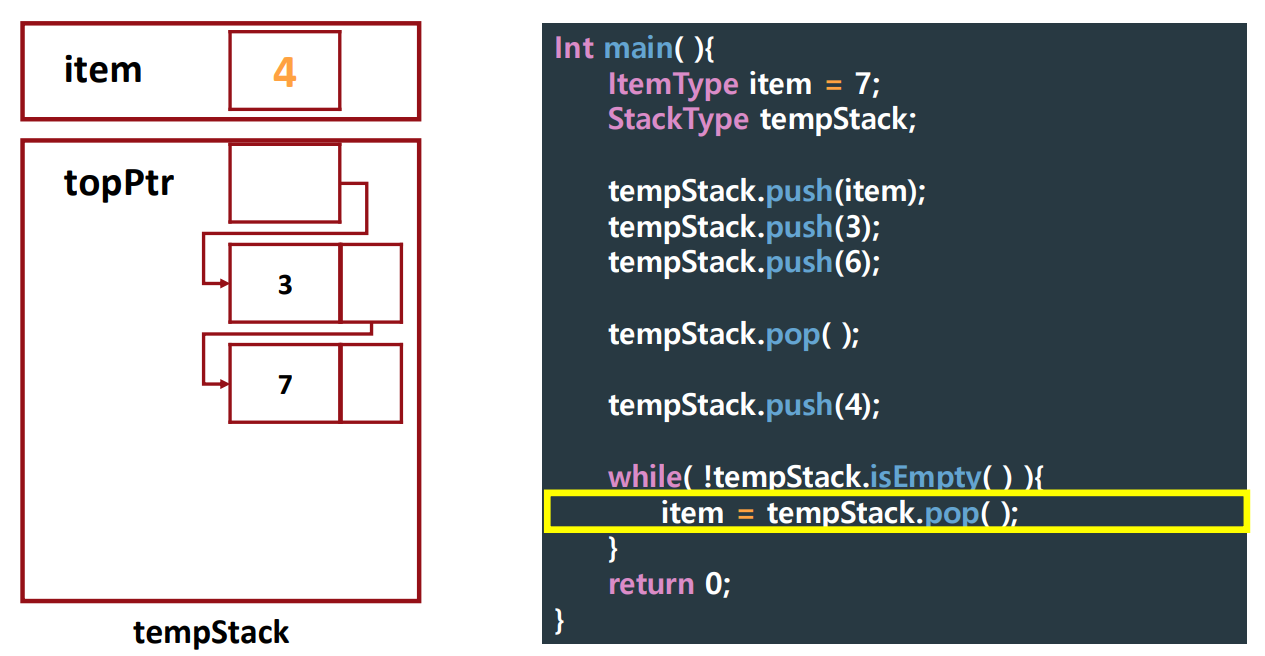

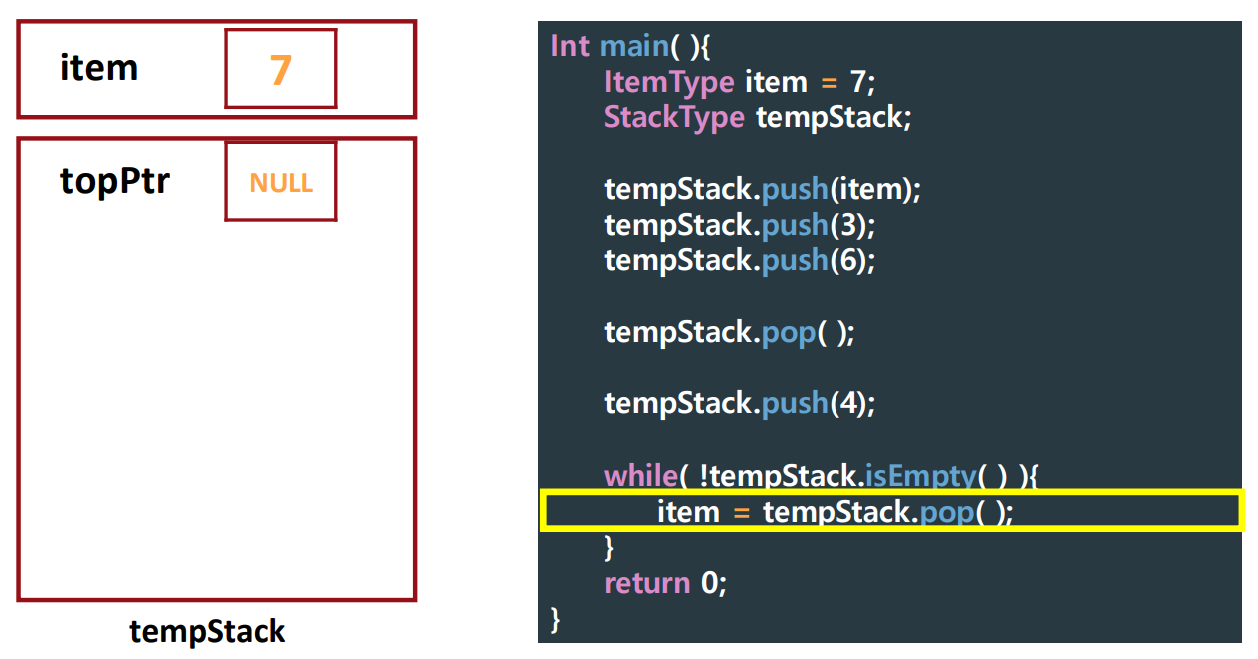
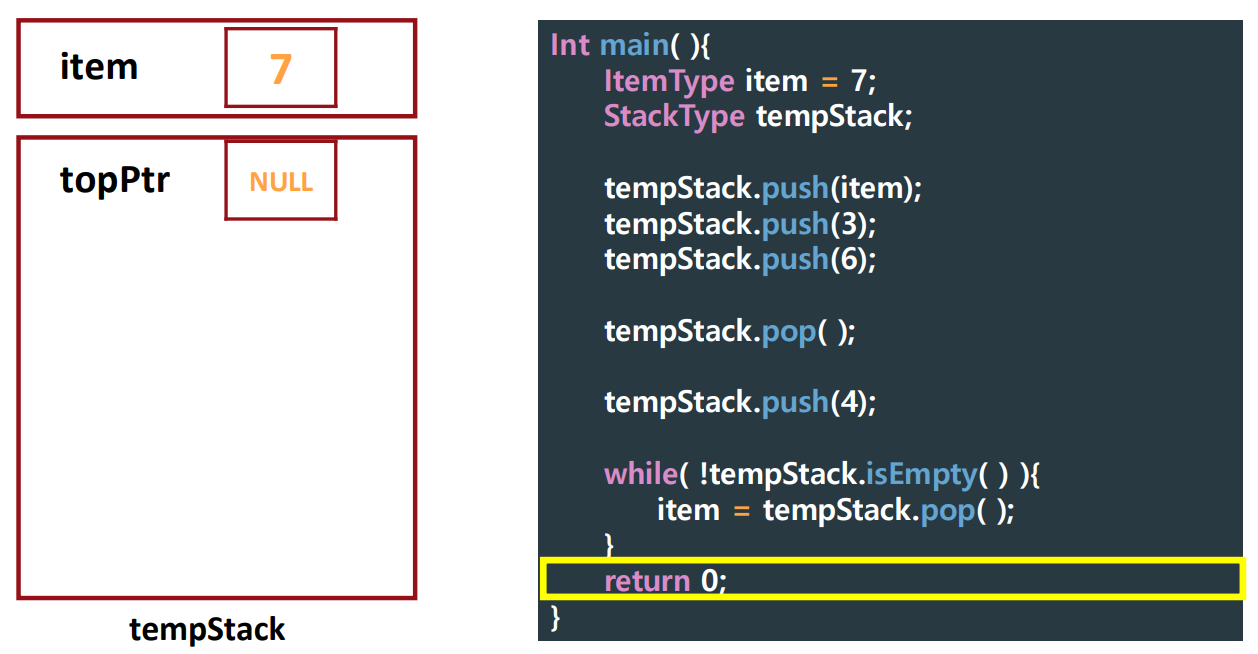
▶ Tracing Client Code
push()
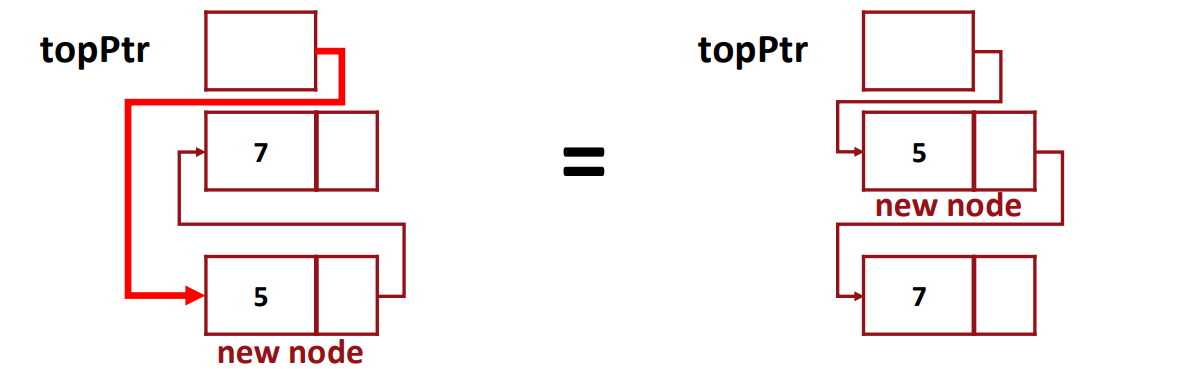
▶ Logical Level
- tempStack.push(5);
0. (Exception Handling)
1. Make a new 'NodeType'
2. Set the new NodeType's 'value' as '5'
3. Make the new NodeType's 'next' point to the old top
4. Make 'topPtr' point to the new Node Type
이때, 3번과 4번의 순서가 바귀면 7이라는 Node를 가리키는 포인터가 존재하지 않게 된다. (메모리 누수 -> 런타임 에러)

▶ Implementation Level
※ 포인터 1 = 포인터 2: 포인터2가 가리키고 있는 걸 포인터 1도 가리키도록 만들라는 의미이다.
Validating Edge Cases
- An "edge case" is a term commonly used in software development to refer to(~을 의미하는) a unique of extreme scenario that deviates from the norm(일반적이지 않은).
- While a program may function well under typcal conditions or inputs, it can encounter unexpected behavior or problems when faced with unusual inputs.
isFull()
Pushing an item generates a new dynamically allocated node.
HEAP is NOT an infinite space.
Operating systems have the default HEAP size for each program, but you can adjust when compiling the code.
When the HEAP is saturated(포화된), 'new' instruction fails and throws an exception.

▶ Implementation Level
pop()

▶ Logical Level
1. Make the topPtr point to the second top node
2. We need to delete the top node (5) .... But we lost pointers pointing to it (topPtr)
3. We need a temporary pointer for it

▶ Logical Level (ver. 2)
0. (Exception Handling)
1. Make tempPtr which points to the top node
2. Make the topPtr point to the second top node
3. Delete the node pointed by tempPtr (tempPtr (local variable) will automatically disappear)

▶ Implementation Level
isEmpty()

▶ Implementation Level
Destructor

▶ Implementation Level
When a local stack variable goes out of scope, the memory space for data member topPtr is deallocated.
But the nodes are NOT automatically deallocated.
clear()

▶ Implementation Level
size()

▶ Implementation Level
Big-O Comparison of Stack Operations
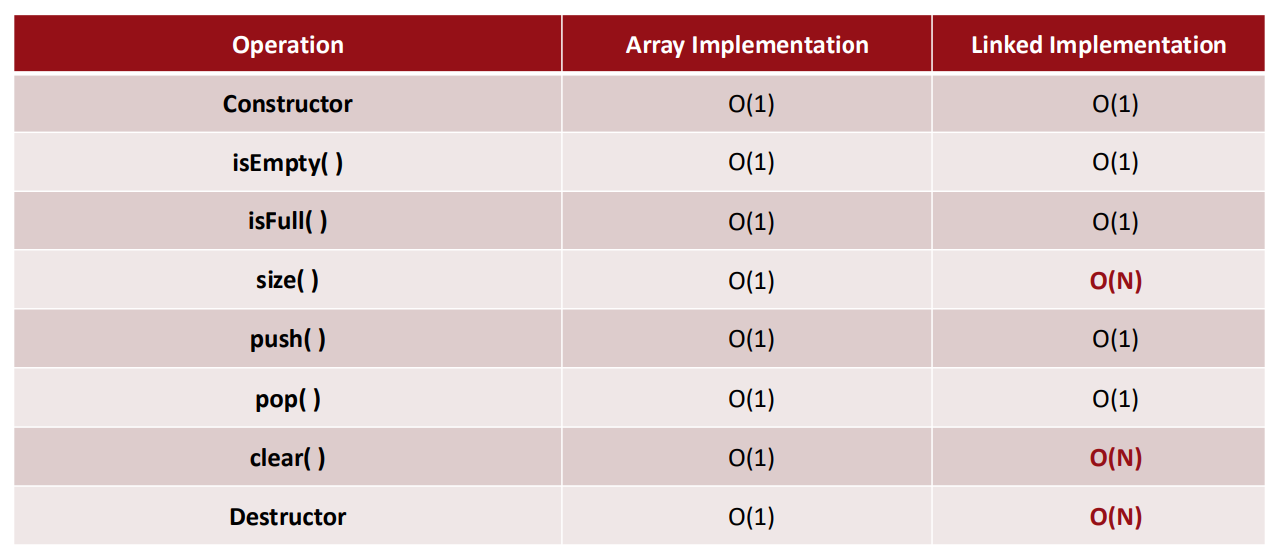
▶ Big-O
Linked Structure (2)
Queue Definition using Nodes

▶ Logical Level

▶ Implementation Level
enqueue()
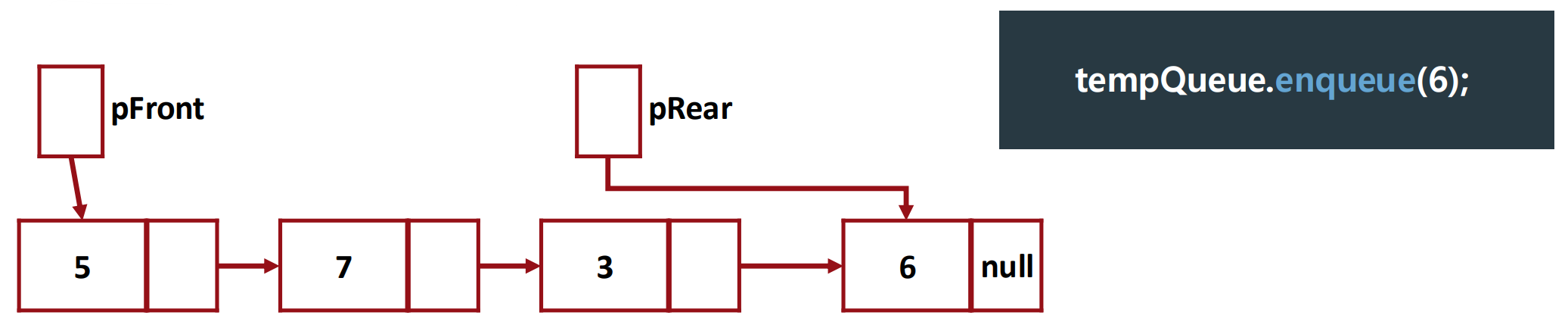
▶ Logical Level
0. (Exception Handling)
1. Make a new 'NodeType' (new node)
2. Set the new node's 'value' as '6' 'next' as nullptr
3. Make the last node's 'next' point to the new node
4. Make pRear point to the new node

▶ Implementation Level
Exception Handling이 필요한 상황
- queue가 full -> enqueue 불가
- queue가 empty -> dequeue 불가
isFull()

▶ Implementation Level
array의 경우에는 size 자체가 고정되어 있기에 full 상태가 명확하고,
linked structure의 경우에도 full 상태가 존재한다.
메모리 상의 heap이라는 공간에도 공간상의 제약이 존재하기에, 위 경우를 full 상태로 본다. (OS의 판단)
enqueue()

▶ Implementation Level: isFull -> Exception Handling
Is it good enough? Let's think about when the queue is empty.
큐가 비어있는 상태에서 enqueue를 하는 경우,
이렇게 완전히 비어있거나, 완전히 꽉 차있거나, 할 때의 Edge Case도 고려해 주어야 한다.

▶ 런타임 에러 발생
- pRear가 가리키는 주소의 next 값을 newNode로 바꿔주려 하는데, pRear는 아무것도 가리키고 있지 않음

▶ 런타임 에러 해결
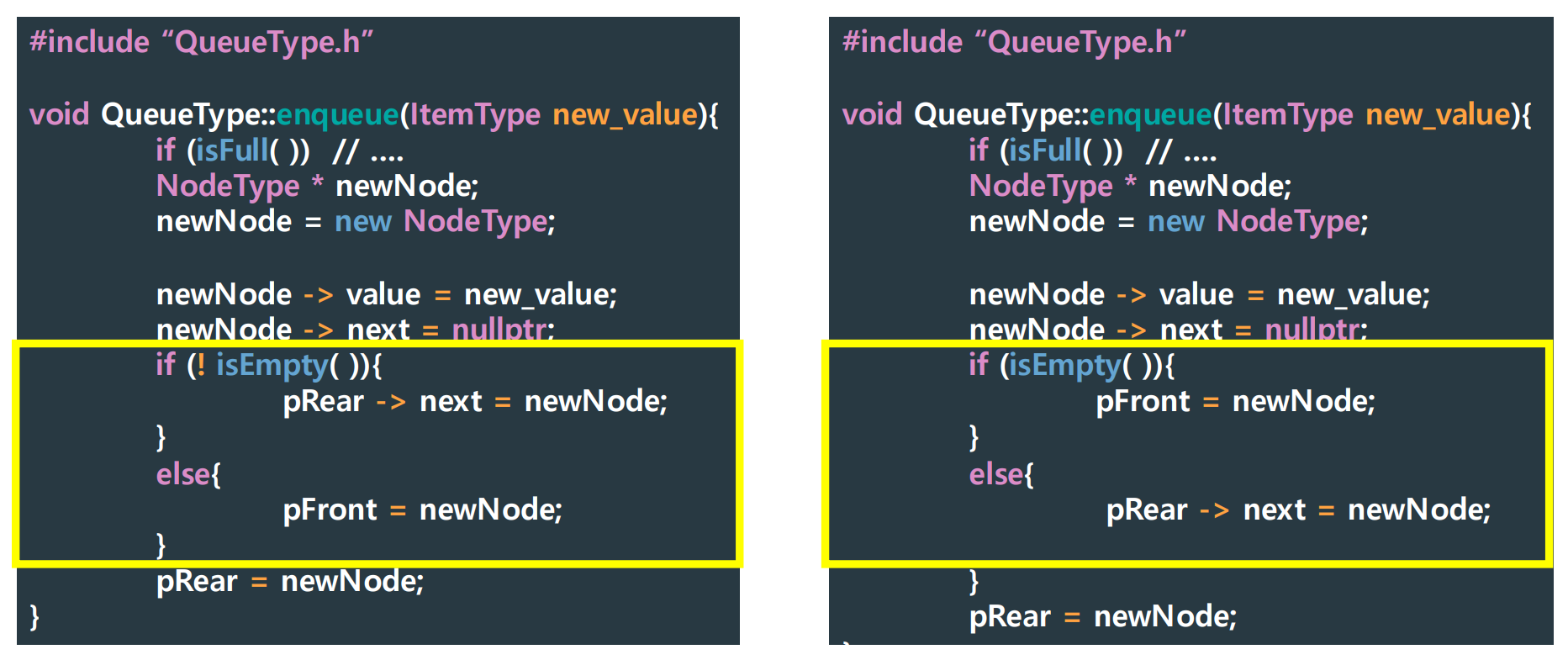
▶ Implementation Level: isFull -> Exception Handling (런타임 에러 해결)
isEmpty()

▶ Implementation Level
dequeue()
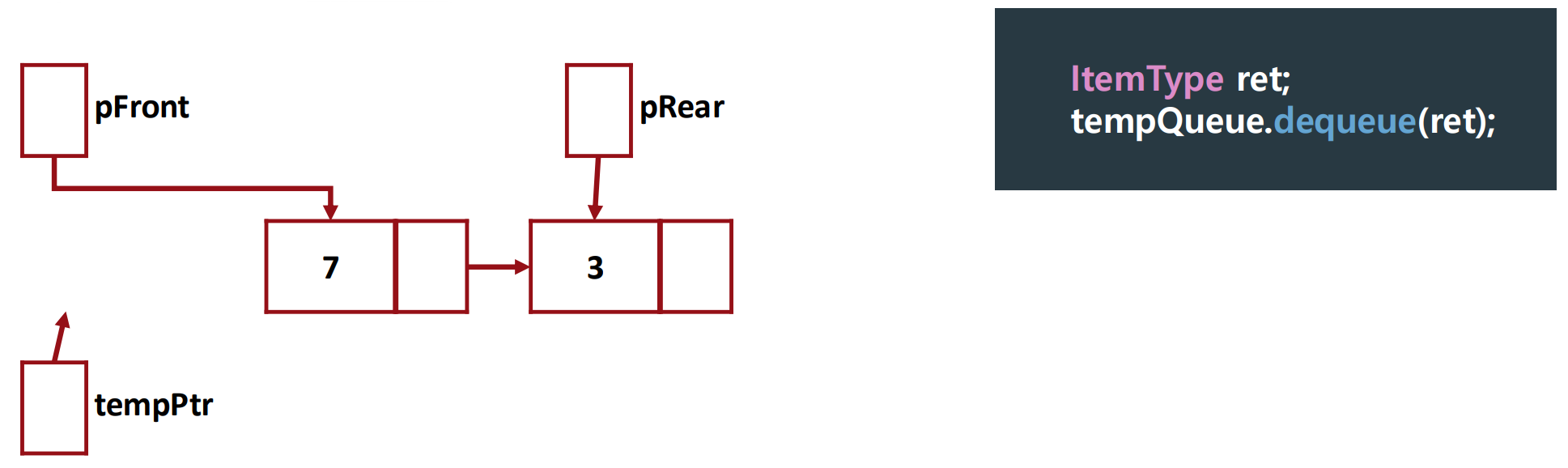
▶ Logical Level
1. Make tempPtr which points to the front node (메모리 누수 방지)
2. Make the pFront point to the second front node
3. Delete the node pointed by tempPtr (tempPtr (local variable) will automatically disappear)
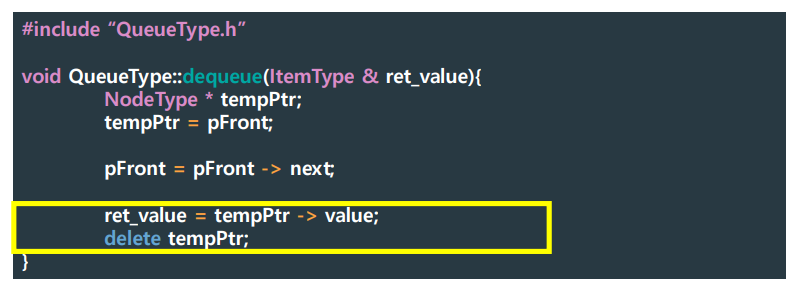
▶ Implementation Level

▶ Logical Level (Edge Case)

▶ Implementation Level (Edge Case)
Destructor and clear()

▶ Implementation Level
이런 식으로 노드 단위로 순환하는 것을 traversal이라고 한다.
※ clear는 주로 flush로 많이 사용한다.
size()

▶ Implementation Level
물론, 이렇게 traverse 하지 않고 length 변수를 따로 만들어 놓을 수도 있다.
위 코드는 length 변수가 없다는 가정 하에 사용하는 방법이다.
Big-O Comparison of Queue Operations
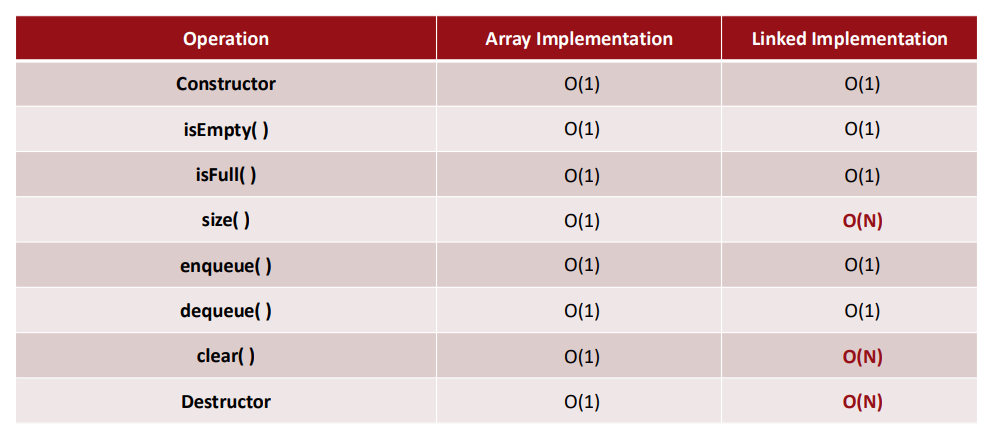
▶ Big-O
- array와 linked structure를 순수하게 시간 복잡도적인 측면에서만 비교하면 array가 더 유리하다.
length 변수를 미리 만들고 enqueue시 length++, dequeu시 length--를 미리 해주면 size()의 시간 복잡도는 O(1)이다.
'CS > 자료구조' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Chapter 6: Linked Structures (2) (5) | 2025.05.20 |
|---|---|
| Programming Exercise: Lab #4 (1) | 2025.04.19 |
| Programming Exercise: Lab #3 (1) | 2025.04.16 |
| Chapter 4.5: Programming Tips (0) | 2025.04.16 |
| Programming Exercise: Lab #2 (1) | 2025.04.06 |