경희대학교 허선영 교수님의 운영체제 수업을 기반으로 정리한 글입니다.
Thread
: 독자적인 실행 흐름
-> 서로 다른 코드 동시 실행 가능하나, 코어당 하나의 thread가 돌아감
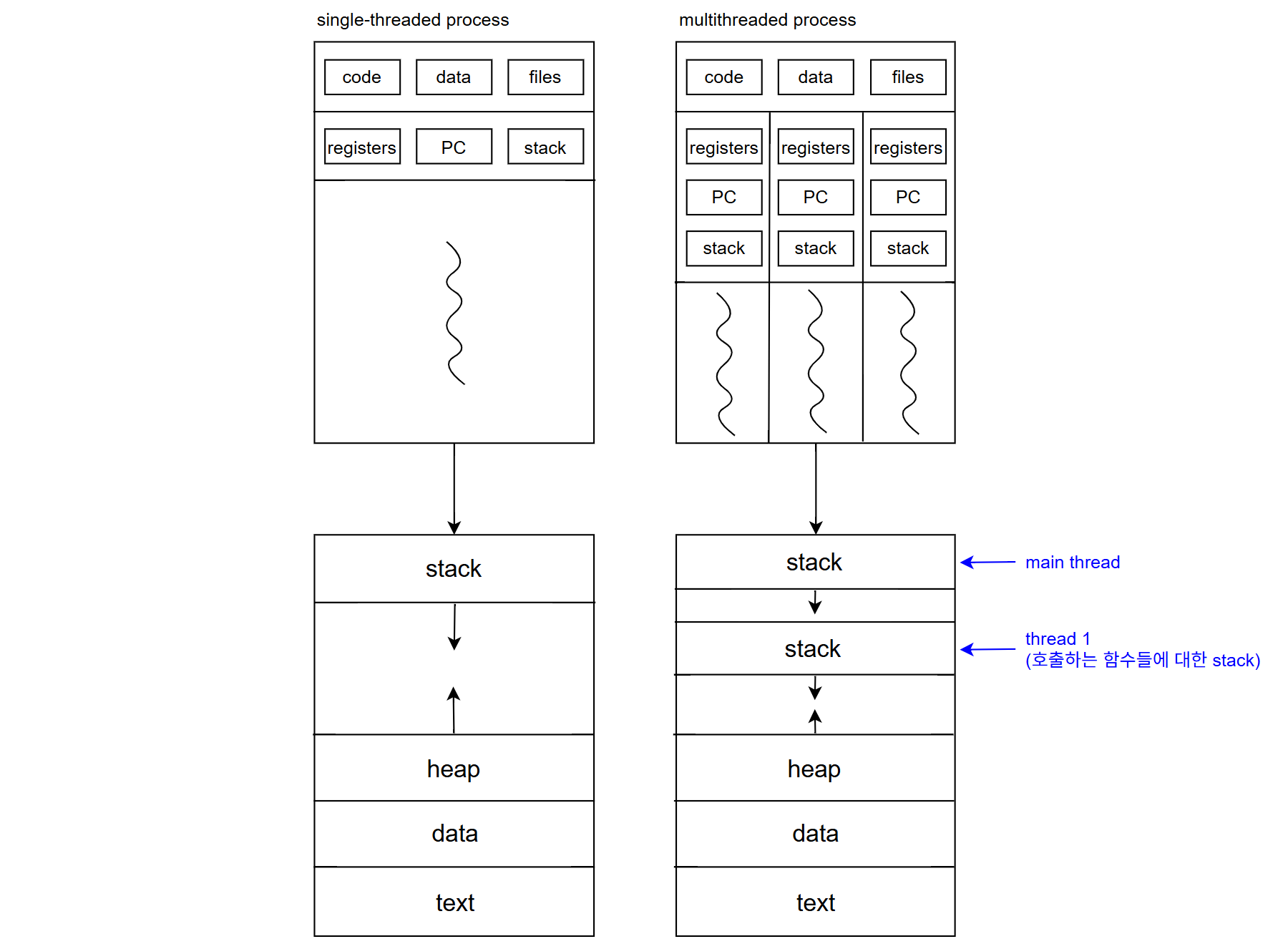
multithreaded processs의 경우, 너무 많은 함수 호출 시 overflow 가능성 더 높다.
※ heap: 프로그램이 전체적으로 관리 및 스레드 간 데이터 공유에도 필요, e.g., 한 스레드가 메모리 할당, 다른 스레드가 사용
Benefits
1. Responsiveness (반응성)
2. Resource Sharing
3. Economy: thread switching lower overhead than context switching
4. Scalability (확장성): multicore일 때 이점

Thread - Use Cases
1. Multithreaded Server Architecture

server(main thread)에서 client는 언제든지 들어올 수 있기에,
client마다 들어왔을 때 thread를 만들어 각각의 client가 평행하게 처리되도록 구현한다.
2. Loop Parallelization on Multi-core System
thread로 쪼개 처리한다.
Parallelism vs Concurrency
1. Parallelism
: 병렬성 -> 여러 스레드를 코어에 나눠 동시 처리
2. Concurrency
: 동시성 -> 싱글 코어에서 thread를 쪼개 동시에 돌아가는 것처럼 보이게 함
- multithreaded/single core -> 번갈아가며 처리
Types of parallelism
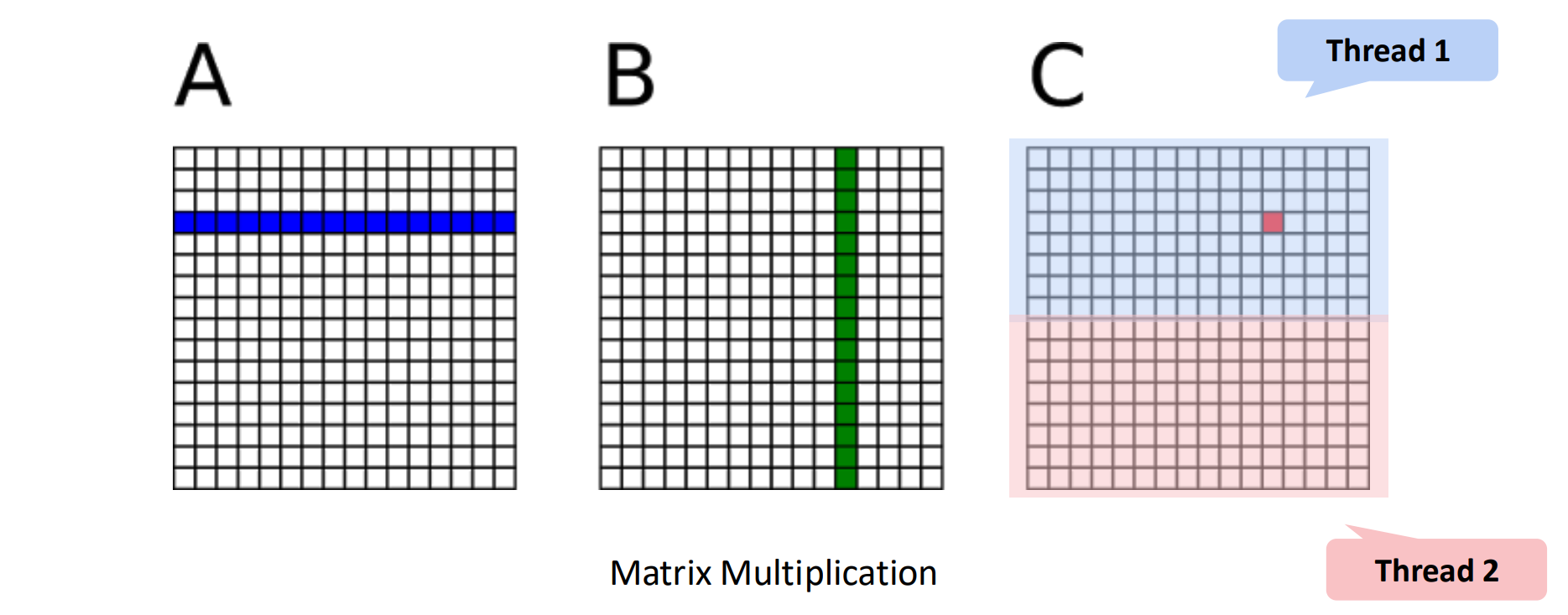
1. Data parallelism
: same operation / different data
- e.g., matrix multiplication

2. Task parallelism
: different operation
- e.g., server architecture
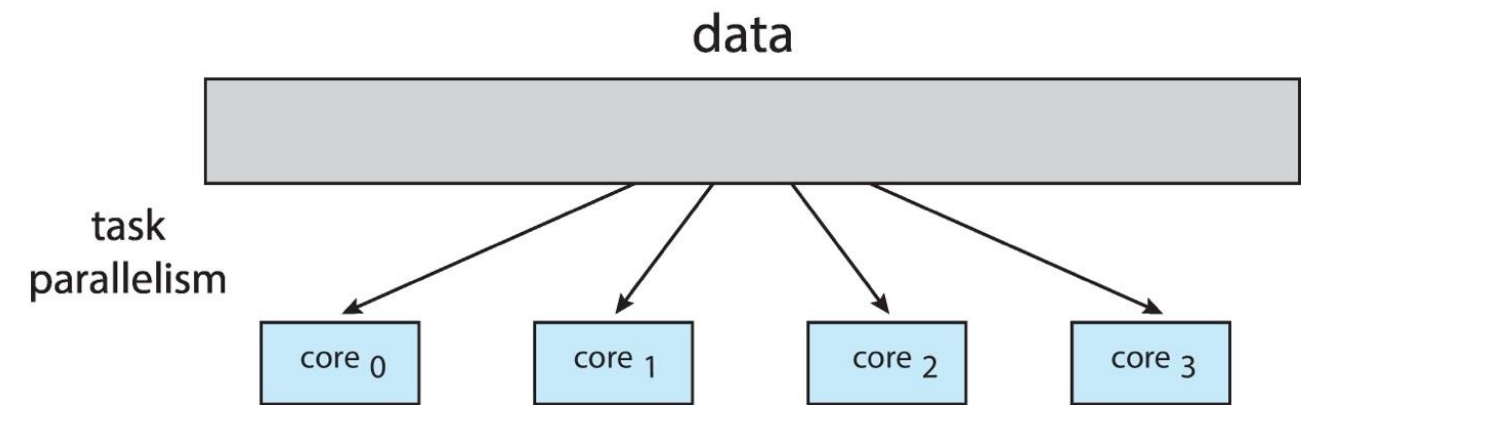
task parallelism은 이벤트를 핸들링하는 시스템에 적합하다.
⭐ Amdahl's Law

- S: Serial portion (직렬)
- N: processing cores
speedup은 "기존 실행 시간 / 코어를 추가해서 얻을 수 있는 실행 시간"으로 계산하는데,
이때 코어가 무한히 많으면 speedup은 1/S로 수렴한다.
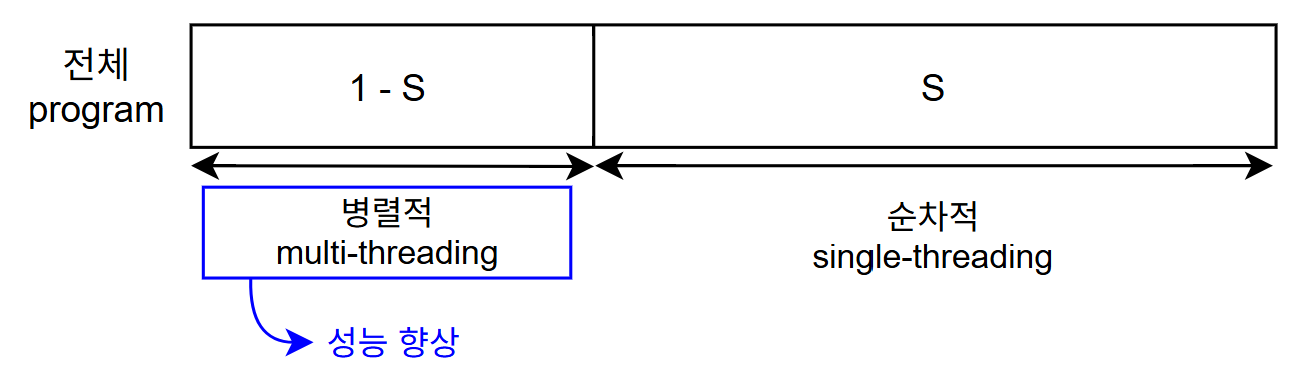
프로그램 최적화: 가장 오래 걸리는 부분을 병렬화
- 아무리 하드웨어가 많아도 병렬화하지 않으면 빠르게 할 수 없기에 프로그램 최적화 위해선 프로그래머 역량 중요
Example)
75% parallel, 25% serial, two cores
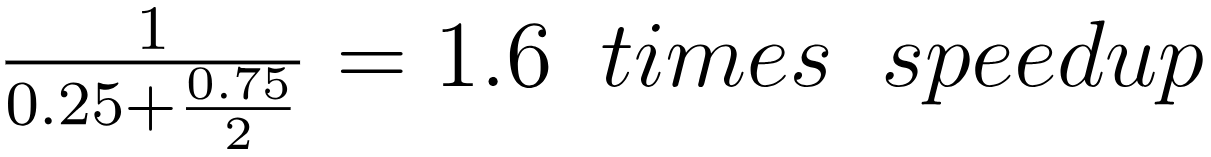
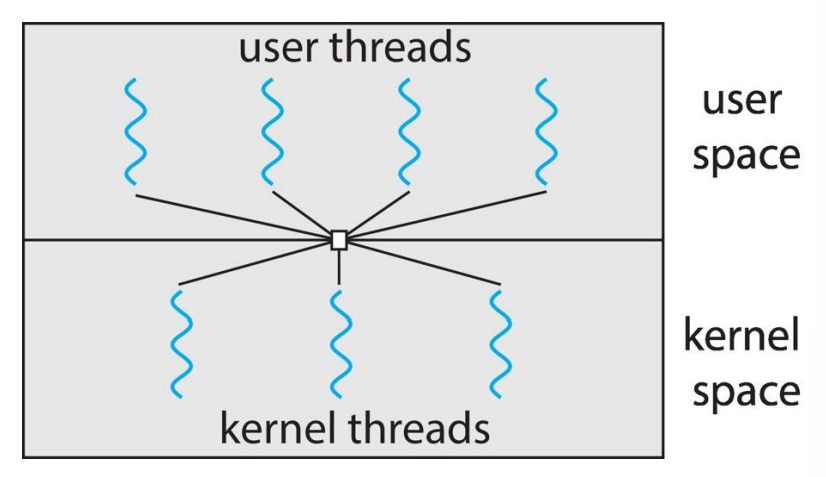
User and Kernel Threads

kernel threads
user threads를 관리하기 위해 실제 CPU에서 돌아가는 threads
-> 실제로 OS에서 스케줄링하는 대상으로, 스케줄러에 따라 일부의 user thread 받아 실행
Multithreading models
1. Many-to-One

only one thread can access the kernel at time
2. One-to-One

more concurrency than many-to-one
-> 스레드가 많을 수록 오버헤드 증가
실제로 가장 많이 사용하는 모델이다.
3. Many-to-Many
자유도가 많지만 구현이 어렵다.
POSIX Pthreads
: thread libraries 중 하나 (POSIX -> 'P'threads)
※ specification, not implementation -> 실제 구현은 OS 개발자가 해야 함
process creation / thread creation


- pthread_join: child thread를 wait -> child tid 받음
Thread Cancellation
: thread 취소 원할 때 사용
1. Asynchronous cancellation: 바로 제거
2. Deferred(미뤄진) cancellation: periodically check
void* runner(void* ){
.
.
.
check [ ] //safe point
}- safe point: pthread_cancel 요청 들어왔는지 확인하여 parent thread가 child thread cancel(종료)
※ 실제 cancellation은 thread 만들 때 설정하는 Mode에 따른 thread state에 따라 thread가 cancel됨
'CS > 운영체제' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Chapter 5: CPU Scheduling (1) | 2025.05.07 |
|---|---|
| Chapter 3: Processes (0) | 2025.05.04 |
| Chapter 2: Operating System Structures (1) | 2025.05.04 |
| Chapter 1: Introduction (0) | 2025.05.04 |